Laboratory guiding principles - Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
Stem cells -- development -- disease-- regenerative medicine
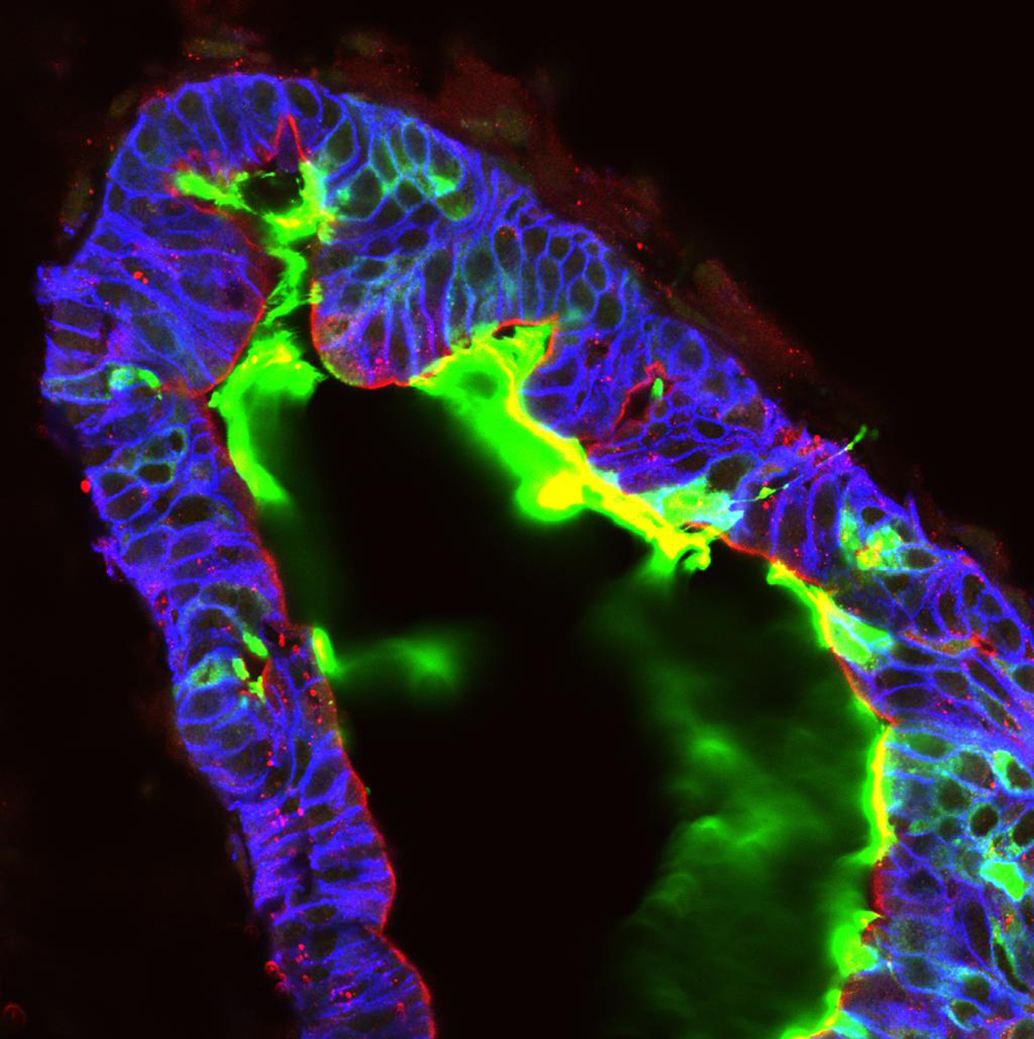
Organogenesis in a dish
The Spence laboratory uses human pluripotent stem cells to generate 3-dimensional tissues in the tissue culture incubator. For example, we generate intestinal tissue, called human intestinal organoids (HIOs) in order to study human intestine development, differentiation and disease.
Using insights from development to build human organs in a dish.
The Spence Lab
The Spence lab was established in September, 2011 at the University of Michigan. We are located in the Biomedical Sciences Research Building (BSRB). The central theme of the lab is to understand how the endoderm and its associated organs develop, with a focus on intestine and lung development.
Embryonic development
The laboratory also uses model organisms to explore the molecular mechanisms that control embryonic development. By understanding how the embryo develops, we gain insights into how abnormal development can lead to congenital disease, or how developmental regulators are involved in regeneration, injury repair or disease in the adult.